Diabetes Quick Guide to Prevent Sugar Crashes: Stay Steady and Thrive
Living with diabetes requires constant vigilance. One of the biggest challenges is managing blood sugar levels. A sudden drop in blood sugar, known as a sugar crash (or hypoglycemia), can be a frightening experience. This Diabetes Quick Guide to Prevent Sugar Crashes will help you understand the causes, symptoms, and how to prevent these episodes. This guide focuses on providing practical, actionable advice. It empowers you to take control of your health.
Sugar crashes aren’t just uncomfortable. They can be dangerous, especially for those with diabetes. Understanding the mechanisms behind sugar crashes is vital. This knowledge allows for proactive management. This guide aims to equip you with the tools needed to avoid these fluctuations. We will explore strategies for maintaining stable blood sugar. This includes dietary adjustments, lifestyle changes, and medication management. It provides a comprehensive approach to prevent crashes.
Understanding Sugar Crashes: The Basics
A sugar crash occurs when blood glucose levels drop too low. This typically falls below 70 mg/dL. This can happen to people with diabetes using insulin or certain medications. These medications are used to manage blood sugar. The body needs glucose for energy. It fuels the brain and other vital organs. When glucose levels plummet, the body struggles to function properly. This can lead to a variety of symptoms. These symptoms range from mild to severe.
Causes of Sugar Crashes
Several factors can contribute to a sugar crash. Understanding these causes is key to prevention. The most common include:
- Insulin or Medication Overdose: Taking too much insulin or diabetes medication can cause blood sugar to drop too low.
- Skipping Meals or Delayed Eating: Not eating on time or skipping meals can lead to low blood sugar. This is especially true if you take insulin or diabetes medication.
- Excessive Exercise: Physical activity burns glucose. Intense or prolonged exercise can deplete glucose stores. This can lead to a sugar crash.
- Alcohol Consumption: Alcohol can interfere with the liver’s ability to release glucose. This can increase the risk of hypoglycemia.
- Unplanned Changes in Diet: Drastic changes in diet, such as eating fewer carbohydrates than usual, can affect blood sugar levels.
Recognizing the Signs: Symptoms of a Sugar Crash
Knowing the symptoms of a sugar crash is crucial. Early detection allows for prompt treatment. This can prevent the crash from worsening. Symptoms can vary from person to person. The severity of symptoms also depends on the blood sugar level. The following are common signs:
- Mild Symptoms:
- Shakiness
- Sweating
- Dizziness
- Hunger
- Headache
- Irritability
- Moderate Symptoms:
- Confusion
- Difficulty concentrating
- Blurred vision
- Weakness
- Rapid heartbeat
- Severe Symptoms:
- Loss of consciousness
- Seizures
- Coma
If you experience any of these symptoms, it is important to check your blood sugar. Treat it immediately if it’s low. If severe symptoms occur, seek immediate medical attention.
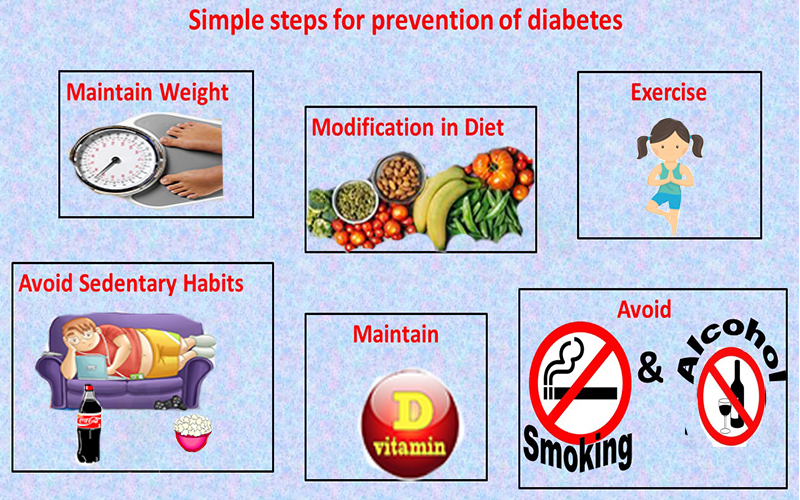
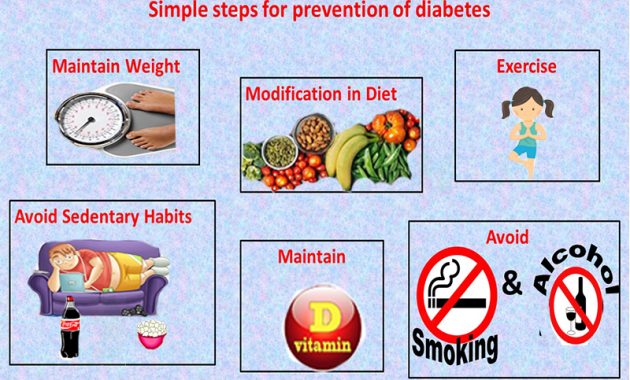
Preventing Sugar Crashes: Practical Strategies
Prevention is the best approach. These strategies can help you avoid sugar crashes. They are essential for managing diabetes effectively.
Dietary Adjustments
Your diet plays a crucial role in maintaining stable blood sugar levels. Consider these dietary modifications:
- Consistent Meal Timing: Eat meals and snacks at regular intervals. This helps prevent fluctuations in blood sugar.
- Balanced Meals: Include a balance of carbohydrates, proteins, and healthy fats in each meal.
- Choose Complex Carbohydrates: Opt for complex carbohydrates. They are digested slowly. This helps prevent rapid spikes and drops in blood sugar. Examples include whole grains, fruits, and vegetables.
- Limit Processed Foods: Avoid sugary drinks, processed foods, and excessive amounts of simple carbohydrates. These can cause rapid blood sugar fluctuations.
- Snack Strategically: Carry snacks with you. They should be readily available. This can help prevent a sugar crash. Good choices include fruit, nuts, or a small serving of yogurt.
Exercise and Activity Management
Exercise is beneficial. However, it can also impact blood sugar. Follow these guidelines to manage exercise safely:
- Monitor Blood Sugar Before Exercise: Check your blood sugar before, during, and after exercise. This helps you understand how your body responds.
- Adjust Insulin Dosage: You may need to adjust your insulin dosage before or after exercise. Consult with your doctor for guidance.
- Eat a Snack Before Exercise: Consume a carbohydrate-rich snack before exercise. This can help prevent low blood sugar.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water. This is especially important during and after exercise.
- Be Aware of Delayed Hypoglycemia: Be aware that low blood sugar can occur hours after exercise. Continue to monitor your blood sugar.
Medication Management
Proper medication management is essential. This is for people taking insulin or other diabetes medications. Work closely with your healthcare provider. They can help you adjust your medication as needed. Consider the following:
- Follow Your Doctor’s Instructions: Take your medication as prescribed by your doctor. Never change your dosage without consulting them.
- Regular Blood Sugar Monitoring: Monitor your blood sugar regularly. This helps you identify patterns. It helps you adjust your medication accordingly.
- Carry Fast-Acting Glucose: Always carry a fast-acting source of glucose. This is for treating a sugar crash. Examples include glucose tablets, juice, or hard candy.
- Educate Others: Inform family, friends, and colleagues about your diabetes. Teach them how to recognize and treat a sugar crash.
Treating a Sugar Crash: Immediate Actions
If you experience a sugar crash, act quickly. Follow these steps:
- Check Your Blood Sugar: Use a blood glucose meter to confirm the low blood sugar.
- Consume 15 Grams of Carbohydrates: If your blood sugar is below 70 mg/dL, consume 15 grams of a fast-acting carbohydrate. Examples include glucose tablets, juice (4 ounces), or hard candy (3-4 pieces).
- Wait 15 Minutes: Wait 15 minutes and recheck your blood sugar.
- Repeat if Necessary: If your blood sugar is still low, repeat the process. Consume another 15 grams of carbohydrates and recheck after 15 minutes.
- Eat a Meal or Snack: Once your blood sugar returns to a normal level, eat a meal or snack. This will help stabilize your blood sugar.
- Seek Medical Attention: If symptoms worsen or you lose consciousness, seek immediate medical attention.
Long-Term Management: Staying Ahead of the Curve
Managing diabetes is an ongoing process. It requires consistent effort and attention. Adopt these long-term strategies for sustained success:
- Regular Check-ups: Schedule regular check-ups with your healthcare provider. This includes your doctor, endocrinologist, and diabetes educator.
- Diabetes Education: Attend diabetes education classes. Learn about the latest management techniques.
- Healthy Lifestyle: Maintain a healthy lifestyle. This includes a balanced diet, regular exercise, and stress management.
- Support System: Build a strong support system. This includes family, friends, and support groups.
- Be Prepared: Always carry a medical ID. This provides crucial information in case of emergencies.
The Importance of Awareness and Proactive Measures
This Diabetes Quick Guide to Prevent Sugar Crashes aims to empower you. It helps you manage your diabetes effectively. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and prevention strategies for sugar crashes is crucial. By taking proactive measures, you can minimize the risk of these episodes. You can also improve your overall health. Remember, consistent monitoring, healthy habits, and open communication are key. They are key for long-term success. Prioritize your health. Take charge of your diabetes. You can lead a fulfilling life. You can live a life free from the fear of frequent sugar crashes. This Diabetes Quick Guide to Prevent Sugar Crashes provides essential information. It will assist in managing your condition. It helps you maintain a stable blood sugar level.
The information provided in this guide is for informational purposes only. It is not a substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult with your healthcare provider. This is for any questions or concerns you may have. They can also provide personalized guidance. They will tailor it to your specific needs. This information is not a substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult with your doctor for appropriate medical care.
[See also: Related Article Titles]